Differences between lists in Unix
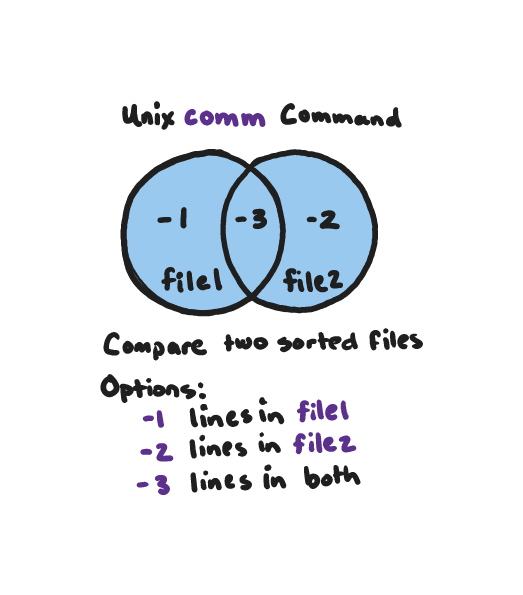
Unix comm command - Difference between two lists
Using the comm(1) command in Unix we can output the difference between sorted lists. The comm command takes two sorted files as inputs and will output lines unique in FILE1, lines unique in FILE2 and lines common to FILE1 and FILE2. The comm command requires the files to be sorted.
Examples
comm -12 file1 file2
Print only lines present in both file1 and file2.
comm -3 file1 file2
Print lines in file1 not in file2, and vice versa.Example with Files
Let’s see an example by creating two lists in file a.txt and file b.txt. Then use the comm command to output what is only in a.txt, in b.txt and in both a.txt and b.txt - the union between them.
Here is an example file named a.txt with contents:
$ cat a.txt
a
b
c
d
eAnother file named b.txt with contents:
$ cat b.txt
a
c
d
e
f
gUsing the comm command we can see the differences between the list in various ways:
$ comm a.txt b.txt
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
$ comm -1 a.txt b.txt
a
c
d
e
f
g
$ comm -2 a.txt b.txt
a
b
c
d
e
$ comm -3 a.txt b.txt
b
f
g
$ comm -12 a.txt b.txt
a
c
d
eNote, in the last example above we can mix the 3 options of 123 to get different outputs.
Additional options
If available the --check-order option will fail if the inputs are not correctly ordered.